Certification and Accreditation in Training and Mentoring
The contemporary job market and education sector impose increasingly higher demands on participants regarding qualifications and the quality of services provided. In response to these needs, certification and accreditation have become key tools in ensuring standards and building trust in both training and mentoring.
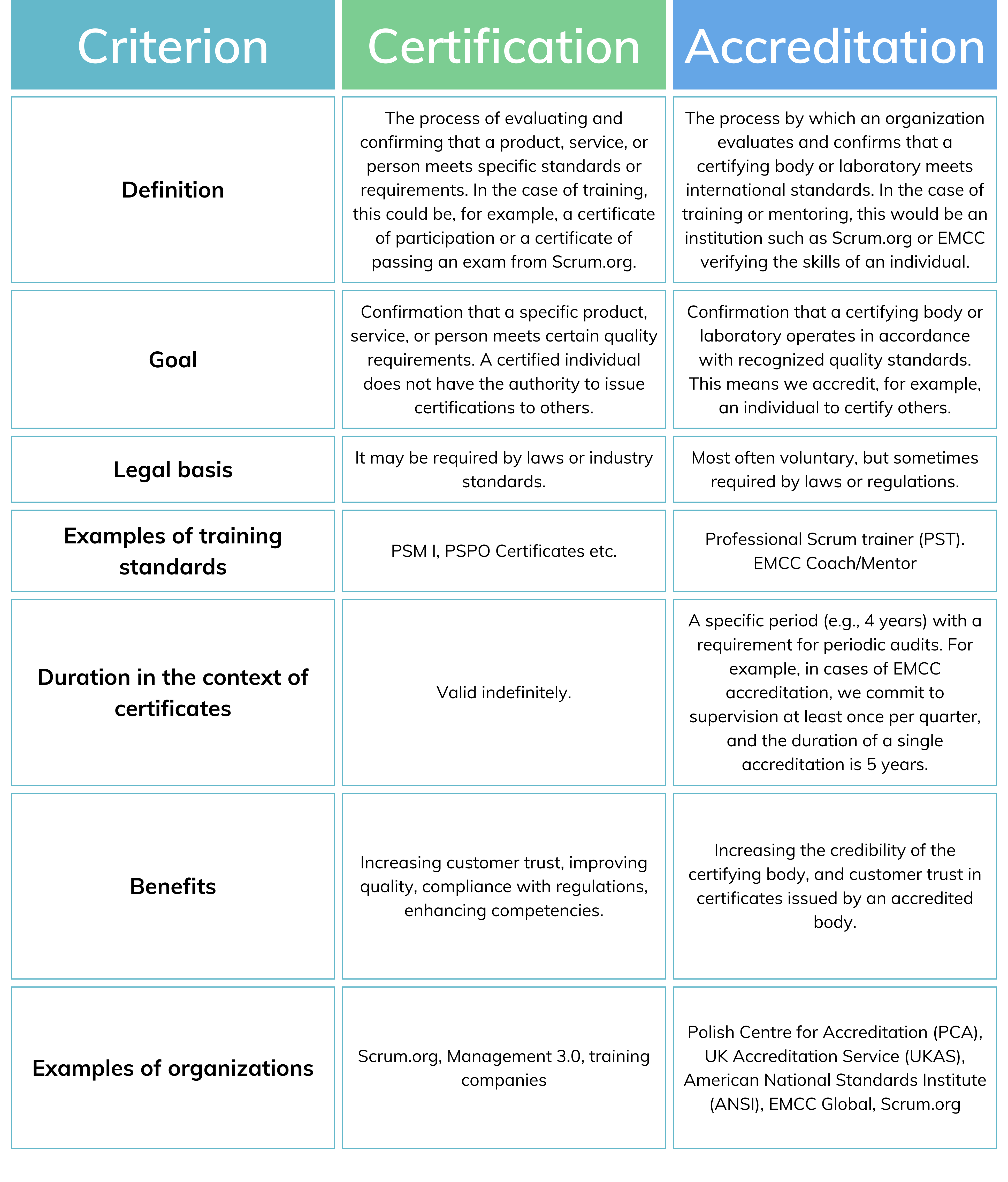
Definition and Goals

Certification is the process of evaluating and confirming that a product, service, or person meets specified standards or requirements. In the context of training, we often refer to certificates of participation or certificates of exams passed in a given field, such as those issued by Management 3.0 or PSM I, PSPO, etc., offered by Scrum.org. The certification process is usually carried out by training companies or trainers themselves and does not authorize the certified person to certify others.
Certification has many benefits for both individuals and organizations. A certificate can be an important asset when seeking a job or career advancement. For organizations, having certified employees is often a marketing asset and proof of high-quality services. Certification also helps maintain high work standards within the organization.

Accreditation
Accreditation is the process of verifying whether a certifying entity or laboratory meets international quality standards. Accreditation is carried out by national or international accreditation bodies, such as the Polish Centre for Accreditation (PCA), UK Accreditation Service (UKAS), or American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
In the educational and mentoring context, institutions such as EMCC or Scrum.org again verify skills but at a different level (in the case of Scrum.org, it is, for example, the accreditation of a Professional Scrum Trainer).
The accreditation process is more complex than individual certification and involves evaluating the entire organization, not just individual courses or persons. An organization seeking accreditation must meet a number of criteria, which include evaluating quality management systems, staff competencies, infrastructure, and operational procedures.
Based on the audit results, the accrediting organization decides whether to grant or deny accreditation. If accreditation is granted, the organization receives formal confirmation that it meets specified quality standards. Accreditation is granted for a specified period and requires regular reviews to ensure continuous compliance with standards.

Accreditation brings numerous benefits to training and certification organizations. It enables them to gain recognition in the market, which can lead to an increase in the number of participants in training programs and customer trust. Accreditation also ensures that the organization operates in accordance with best practices and is regularly evaluated for quality. Thanks to accreditation, organizations can access funds and grants. It can also facilitate collaboration with other educational institutions and industry organizations.
Who Conducts It?
Certification in the context of training and mentoring is usually conducted by training companies or certifying organizations that offer educational programs and issue certificates confirming course completion and the acquisition of specific skills. These organizations can be both private and public.
Private training organizations often operate within specific industries and offer specialized courses tailored to market needs. Examples include IT training companies that offer certificates in programming, IT product management, network security, etc.
Public certifying organizations, such as universities and higher education institutions, also offer educational programs ending in certification. These institutions typically have larger resources and infrastructure, allowing them to conduct more comprehensive training programs. Certificates issued by public educational institutions are often widely recognized and valued in the job market.
Certification and Accreditation in Mentoring and Training
Certification in mentoring aims to recognize the mentor's competencies, increasing their credibility and trust from clients and training program participants. Mentors who have undergone the certification process can boast formal recognition of their skills and knowledge, making them more attractive to those seeking support in professional or personal development.
Mentor certification includes evaluating their communication skills, ability to build relationships, and knowledge of management and personal development. This process often involves exams, workshops, and practical assessments, during which mentors must demonstrate their skills in real-life mentoring situations.

Accreditation, on the other hand, ensures that the training institution has the appropriate resources, structures, and processes to ensure high educational standards. Training organizations that have obtained accreditation are recognized as institutions meeting the highest quality standards. This process includes evaluating various aspects of the organization's functioning, such as the quality of teaching staff, curricula, infrastructure, and quality management systems.
Requirements
Certification
The requirements for certification are usually specified by training organizations and may include various criteria:
- Course completion: Courses can be offered in various forms, such as on-site classes, online courses, workshops, or seminars. Training programs are often organized into modules that must be completed within a specified time.
- Passing exams: Exams can take the form of written tests, multiple-choice tests, practical tasks, or oral exams. Depending on the field, the exam may include both theoretical knowledge and its practical application.
- Demonstrating practical skills: Candidates often have to demonstrate practical skills by completing projects, case studies, simulations, or practical tasks.
- Verification of experience: In some cases, especially in professional certifications, candidates must document their previous work experience. This may include providing references, employment history, portfolios of completed work, or evidence of participation in projects.
Accreditation
For accreditation, the requirements are more complex and concern the entire organization. The accreditation process assesses not only the quality of the educational programs offered but also the overall ability of the organization to achieve its educational goals at a high level:
- Quality management systems: This includes implementing evaluation procedures, monitoring results, and corrective actions in the event of identified problems. The quality management system should comply with recognized standards, such as ISO 9001.
- Staff competencies: Instructors, trainers, and mentors must have appropriate professional qualifications, experience, and pedagogical skills. The teaching staff should regularly participate in professional development training to maintain their competencies at a current level.
- Infrastructure: This includes the availability of appropriate lecture rooms, laboratories, libraries, technological resources, and educational materials. The infrastructure should be tailored to the specifics of the training programs and the number of participants.
- Operational procedures: These should include managing recruitment, registration, participant evaluation, course organization, and administrative support. All procedures must comply with applicable laws and accreditation standards.
- Compliance assessment: The compliance assessment process includes audits, documentation reviews, on-site visits, and interviews with employees and program participants.
- Continuous improvement: Accreditation requires organizations to continuously strive to improve their processes and educational programs. This includes regular reviews and updates of curricula, implementing innovative teaching methods, and responding to changing market and participant needs.
Process
Certification
The certification process includes evaluating a specific course or person and then issuing a certificate confirming that the specified requirements have been met.
- Registration and application: The candidate must provide the necessary documents, such as proof of education, work experience, and any other required qualifications.
- Documentation review: The initial assessment involves reviewing the submitted documentation to ensure that the candidate meets the basic requirements to proceed to the next stages of certification. This is a formal verification stage where aspects such as compliance with initial requirements and completeness of submitted documents are checked.
- Theoretical and practical exams: Theoretical exams test knowledge in a given field, while practical exams assess the ability to apply this knowledge in practice. For example, in the case of professional certification, the practical exam may include simulations of real professional tasks.
- Practical skills assessment: The candidate must demonstrate the ability to perform specific tasks under conditions close to reality. This may include skill demonstrations, group work, presentations, or projects. Assessments are usually conducted by experienced specialists in a given field.
- Documentation verification: This involves detailed checking of all presented evidence confirming the candidate's qualifications. This process may include contacting previous employers, verifying the authenticity of certificates and diplomas, and checking compliance with applicable standards.
- Issuing the certificate: After successfully completing all assessment stages, the candidate receives a certificate confirming that the specified requirements have been met.
- Validity period and renewal: The renewal process may (but does not have to) include participation in additional training, earning educational points, and retaking exams. Certificates such as PSM I or PSPO issued under the Scrum framework are valid indefinitely.
Accreditation
Accreditation is a more complex and lengthy process that involves evaluating the entire organization.
- Accreditation application: This is submitted to an independent accreditation agency. The application contains detailed information about the organization, its structure, training programs, staff, and quality management procedures.
- Self-assessment of the organization: This step allows identifying strengths and weaknesses as well as areas requiring improvement. Self-assessment is often supported by preparing detailed reports and documentation.
- Documentation review: The accreditation agency conducts a detailed review of the documentation provided by the organization. This review includes evaluating compliance with established quality standards, policies, procedures, and self-assessment results.
- External audits: A key element of the accreditation process is external audits conducted by independent experts. These audits may include on-site visits, interviews with employees and training program participants, and observation of the organization's actual operations.
- Staff and infrastructure assessment: This assessment includes checking the qualifications and competencies of the teaching staff as well as the availability and quality of educational infrastructure, such as lecture rooms, laboratories, libraries, and technical resources.
- Audit report and recommendations: After the audit, the evaluation team prepares a detailed report containing the assessment results, conclusions, and recommendations for areas requiring improvement. The organization may be required to implement the recommendations before accreditation is granted.
- Accreditation decision: Based on the audit results and the report, the accreditation agency decides whether to grant or deny accreditation. This decision is formally communicated to the organization along with justification and, if necessary, further steps.
- Regular reviews and maintaining accreditation: Accreditation is granted for a specified period, usually from several years to a decade, and requires regular reviews. Organizations must regularly provide progress reports and may be subject to additional audits to ensure continuous compliance with quality standards.
Accreditations, such as those granted by EMCC for coaches and mentors, have a specified validity period — often four years, after which renewal is required. This process typically includes regular audits and supervision (e.g., quarterly), ensuring the continuity of standards and the quality of services provided. For example, a single accreditation period under EMCC can last up to five years, requiring institutions or professionals not only to maintain high standards but also to regularly confirm and improve them.